서강대 신관우 교수님이 광합성 인공 세포에 관한 내용으로 Nature Biotechnology에 논문을 내셨군요^^
(원문)
ABSTRCT
Inside cells, complex metabolic reactions are distributed across the modular compartments of organelles1,2. Reactions in organelles have been recapitulated in vitro by reconstituting functional protein machineries into membrane systems3,4,5. However, maintaining and controlling these reactions is challenging. Here we designed, built, and tested a switchable, light-harvesting organelle that provides both a sustainable energy source and a means of directing intravesicular reactions. An ATP (ATP) synthase and two photoconverters (plant-derived photosystem II and bacteria-derived proteorhodopsin) enable ATP synthesis. Independent optical activation of the two photoconverters allows dynamic control of ATP synthesis: red light facilitates and green light impedes ATP synthesis. We encapsulated the photosynthetic organelles in a giant vesicle to form a protocellular system and demonstrated optical control of two ATP-dependent reactions, carbon fixation and actin polymerization, with the latter altering outer vesicle morphology. Switchable photosynthetic organelles may enable the development of biomimetic vesicle systems with regulatory networks that exhibit homeostasis and complex cellular behaviors.
http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&oid=009&aid=0004158697&sid1=001&lfrom=memo
스스로 광합성하는 인공세포 개발
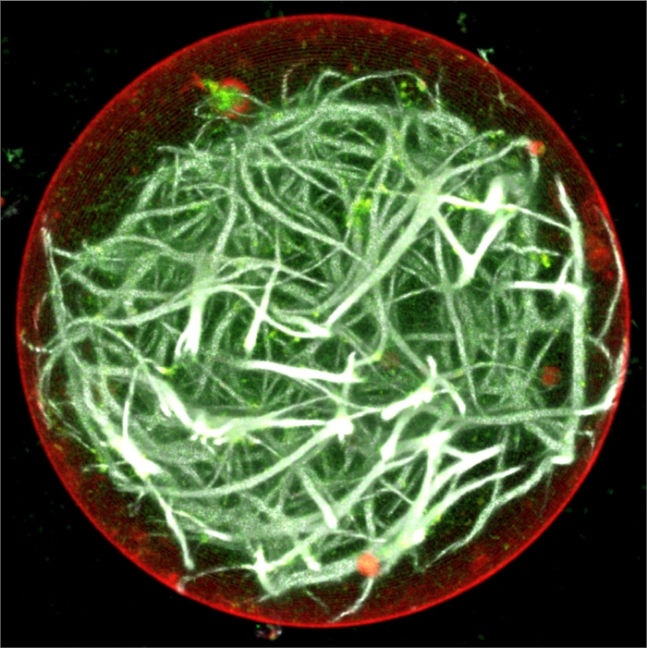
연구진이 개발한 인공세포 모습국내 연구진이 주도한 국제 공동 연구진이 살아있는 세포와 동일한 형태와 기능을 갖고 있는 인공세포를 제작하는데 성공했다.
신관우 서강대 화학공학과 교수와 케빈 파커 미국 하버드대 교수 등 공동 연구진은 세포와 동일할 뿐 아니라 스스로 에너지를 생산해 낼 수 있는 인공세포를 만드는 데 성공했다고 밝혔다. 연구결과는 국제학술지 ‘네이처 바이오테크놀로지’ 28일자(현지시간)에 게재됐다.
연구진은 시금치에서 광합성 단백질을, 박테리아에서 광전환 단백질을 추출한 뒤 세포와 유사한 형태로 재조합해 인공세포를 만들었다. 개발된 세포는 빛을 사용해 스스로 생체에너지(ATP)를 만들어냈으며 세포의 움직임과 형태를 구성하는 세포골격으로 만들어냈다. 또한 빛에 반응해 스스로 움직이기도 했다. 신관우 교수는 “이는 마치 원시적 형태의 살아있는 세포와 유사하다”며 “살아있는 생명체에 가장 근접한 인공세포를 만들어낸 것”이라고 설명했다.
세포는 외부 빛이나 영양분을 흡수해 성장에 필요한 다양한 물질을 스스로 만들어낼 수 있다. 세포를 독립적인 생명체라고 부르는 이유다. 이처럼 세포 내에서 일어나는 다양한 대사활동은 에너지를 흡수하고 전환하는 복잡한 과정으로 구성되어 있어 모사하기 어려운 분야로 알려져 있다. 연구진이 개발한 인공세포는 마치 살아있는 세포에 존재하는 ‘미토콘드리아’처럼 외부에서 빛을 쪼여줄 경우 ATP를 만들어냈다. 외부환경에 따라 최소 한달까지 지속적으로 대사활동을 하며 광합성을 했다. 신관우 교수는 “진화 초기 단계의 세포와 매우 유사한 형태로 현재까지 인공적으로 구현된 세포 중 가장 진화한 형태와 기능을 갖고 있다”고 설명했다.
연구진은 이번에 개발한 인공세포가 실제 세포와 유사한 만큼 생화학·의학 연구에 적용할 수 있을 것으로 기대하고 있다. 신관우 교수는 “세포 내에서 벌어지는 다양한 의학적 부작용이나 대사활동의 비정상적인 활동 원인을 밝혀내는데 활용할 수 있다”며 “또한 기능이 저하된 세포를 대체할 수 있는 기능성 세포의 제작과 인공적으로 배양된 장기와 조직을 구현할 수 있도록 하는 가장 핵심적인 기술을 제공할 수 있을 것”으로 내다봤다.